Explain the importance/ objectives/ role of marketing channels.
 Email This Post
Email This Post
Marketing channels from the soul of the marketing function. Consider a product of customer’s choice made by a manufacturer at the right price. Now when a customer wants to buy the product, he will have to locate a manufacturer who may be in a different region. Just making enquiries about the product, getting it, etc. will take immense effort from the customer. It has been noted that most of the products in the market fail if they are not made available to the target customer at the right time and at the right place. The roles, functions and benefits of marketing channels are listed below-
1) When the product information is available (promotion), the customer is bound to make enquires with different retailers, ecommerce sites, wholesalers, etc. It becomes important for the manufacturers to ensure the product is easily available to the customers. Else a competitor will take advantage of this opportunity and introduce the product with different intermediaries for the customer.
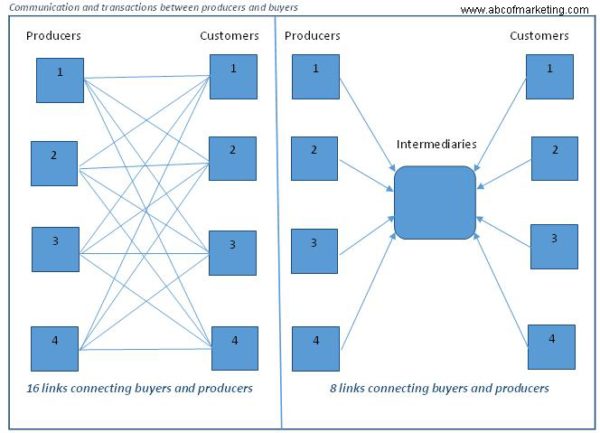
2) Presence of intermediaries reduces the number of links between the manufacturers and the buyers. As shown in the figure, for example, if the producer 1 manufactures shirts and producer 2 manufacturers shoes. So a customer looking for both these items will have to contact these 2 manufacturers separately. This effort will be greatly reduced if both of these items are available with an intermediary like a retailer. This not only benefits the customer but also the manufacturer in meeting its marketing strategy, sales, etc.
3) The presence of the marketing channels ensure market coverage and a successful marketing strategy for the organisation. The intermediaries provide a variety of products from different manufacturers at one place. The customer doesn’t needs to make extra efforts to reach the manufacturers. The intermediaries not only provide producers products but also act as hub of information about the products and manufacturers. A customer can get all the required information on the product like its features, quality, warranties, guarantees, and also have a first-hand experience of experiencing the product via demo.
4) The intermediaries provide a variety of products at one place. The buyers get a great opportunity of comparing the products and their substitutes from different manufacturers.
5) The intermediaries perform the function of product storage as well as transportation. In their absence, the manufacturer will have to perform these functions. They take the risk of transportation and storage.
6) The intermediaries reduce the transaction costs because of the lower number of links between manufacturers and buyers.
7) They are the source of information for manufacturers. The intermediaries provide information about the market like demand, competitors, consumer behaviour, consumer buyer behaviour, etc. (marketing environment) which helps manufacturers in altering marketing strategies or identifying new needs and wants in the market (information on opportunities and threats).
8) Intermediaries take the risk of new product launches. Irrespective of the acceptance of a new product in the market, the intermediaries take the risk of managing the new product that requires investment in time, effort and money.
9) Time utility function – the intermediaries perform the function of making the product available at a convenient time.
10) Place utility function – the product is made available at a convenient location.
11) Products are made available in small as well as large quantities – Break of bulk services. For example, a customer can buy a single tooth brush or half-a-dozen at a time from an intermediary. To entertain each and every request of different quantities from the buyers in the marketwill be a difficult task for the manufacturer.
12) The intermediaries help promote products via different in-store promotion activities like distribution of pamphlets, display, assigning shelf space, store salesman, etc. For example, customers do ask the store representatives about the value of the product, any complaints from other customers, etc.
13) Knowledge of the region – a manufacturer will need help of local people in the target market on the expertise on the local language, culture, etc. The retailers, etc. perform this function, and help the manufacturer in implementing its marketing strategies.
We can conclude that the presence of intermediaries, middlemen or resellers fill the below gaps between the manufacturer and the consumer-
a) Space gap – manufacturer location is at different location from the buyer. Intermediaries make the product available at the convenient place to the buyer.
b) Time gap – As manufacturing takes place at a different place from the buyer’s location, product reaching the buyers place at the time of need is not possible. Intermediaries store the products in advance to ensure the product is readily available when needed.
c) Offerings gap – Intermediaries store different kinds of goods from same as well as different manufacturers. The customer can buy groceries, clothes, shoes, etc. from a single retailer now days. For example, shopping malls, supermarkets, etc.
d) Quantity gap – Products are made available in small as well as large quantities.
e) Information gap – Intermediaries educate the customer about the product through demo, etc. This function helps buyers to compare different products, understand the value delivered by the product, etc.
f) Product variety gap – Intermediaries store goods from different manufacturers. Buyers don’t need to contact the manufacturer individually for comparison, etc.
The manufacturer can decide to skip the intermediaries. Usually large organisations directly sell to consumers like Apple store, Vodafone mini store, etc. Here the manufacturer saves the costs on intermediary margins and reduces the cost of the product. The lower cost increases the profit margins. Some examples are direct selling through company sales representatives, mail, vending machines, phone calls (telemarketing), infomercials, internet selling, etc.